Learning React - Building up the user interface using components and dummy data
In the last post you saw how we’d spun up a new React project that would eventually go on to connect to an existing ASP.NET Core Web API.
We’d got as far as one simple component and needed to finish off our basic interface and hook it up to some data.
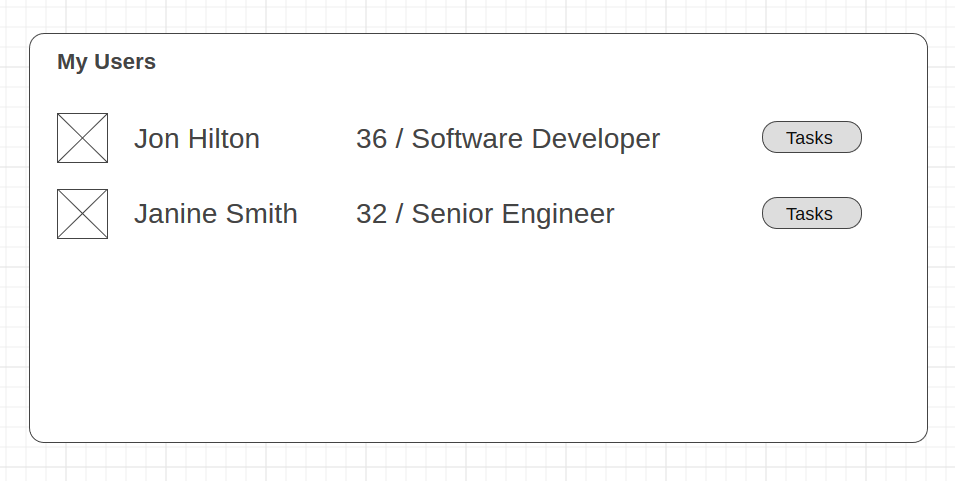
Here’s a quick reminder of what we were aiming for.
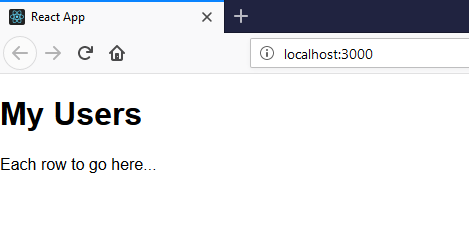
And this is how far we’d got.
So where next?
Components all the way down#
One of the pillars of React is that everything is a component.
Building any user interface in React boils down to deciding which components you need and what order to build them in.
Our simple list of users could be one big component with all the markup and logic in one file but React encourages you to break this down.
A better bet is to build several smaller components, each with one specific role, which you can develop in isolation and then arrange together to form your bigger all singing and dancing feature.
And when you stop to think about it, this makes perfect sense.
It’s flippin difficult to build an entire application in one go, but break it down into manageable chunks and you’ll find you blitz through the requirements like nobody’s business.
Building the user details row#
With this in mind we set about building a simple component to show user details for each user (as rows in our My Users list).
Here’s what we ended up with.
UserRow.tsx
import * as React from "react";
function userRow() { return ( <tr> <td className="avatar">Avatar</td> <td className="name">Jon Hilton</td> <td className="summary">36 / Lead Developer</td> <td className="actions">Buttons here</td> </tr> )}
export default userRow;Here we’re sticking with a simple ethos of getting the key elements in place first before worrying too much about appearance (hence using a simple table; I could easily get lost for days trying to make anything work using CSS!).
We’re still using hardcoded values and before moving on to real data needed to plug at least one of these rows into our MyUsers component.
MyUsers.tsx
import * as React from "react";import UserRow from "./UserRow";
export default class MyUsers extends React.Component<any, any>{ public render() { return ( <div> <h1>My Users</h1> <table className="user-list"> <tbody> <UserRow /> </tbody> </table> </div> ); }}A small tweak here to render everything using a table and to bring in our shiny new UserRow component.
We put some minimal css in index.css…
.user-list { width: 600px;}
.avatar { max-width: 100px;}
.name { padding-left: 10px; max-width: 600px;}
.summary { padding-left: 10px; max-width: 400px;}
.actions { max-width: 100px;}Checking our progress now gave us this…
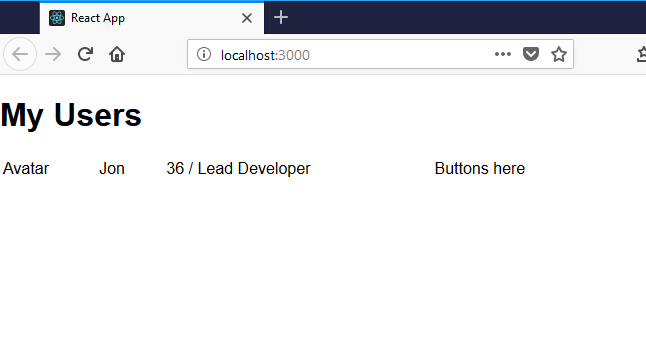
So far so good, but what about driving this row from some actual data? (not just hardcoded values in the markup).
Props to you#
We needed to take this…
import * as React from "react";
function userRow() { return ( <tr> <td className="avatar">Avatar</td> <td className="name">Jon Hilton</td> <td className="summary">36 / Lead Developer</td> <td className="actions">Buttons here</td> </tr> )}
export default userRow;And make it possible to render multiple rows, each with their own values for each cell.
Legacy .NET web apps causing you grief?
Build modern, reliable web applications, faster with .NET and Blazor.
Build better .NET web appsNow if you’re used to working with ASP.NET MVC and Razor, you’re no doubt used to referencing @Model to render values…
<p>Hey @Model.FirstName!</p>React’s equivalent is “props”…
import * as React from "react";
export default class UserRow extends React.Component<any, any>{
public render(){ return ( <tr> <td className="avatar">Avatar</td> <td className="name">{this.props.user.name}</td> <td className="summary">{this.props.user.summary}</td> <td className="actions">Buttons here</td> </tr> ) }
}Assuming we could somehow get that user object into our component, the “name” and “summary” values would be rendered in their correct locations within the markup.
NOTE
Exercise caution when cheating with any
If you’ve used Typescript at all you’ve probably spotted a little bit of cheating going on here…
React.Component<any, any>
The first <any, indicates what type our props are.
By using any we’re basically saying the props can be of any type. Doing this enables us to get something up and running quickly but also removes the type safety we’d otherwise get.
If we specified a type there instead, the typescript compiler would protect us from ourselves, ensuring we have to pass an object of the right “shape” to our component.
However this was enough to get us going and we could always add the types once we’d learned the ropes…
Now we could pass a “user” to our component like so…
let someUser = { id: 1, name: 'Jon', summary: '36 / Lead Developer' };
/// code omitted
<UserRow user={someUser} />But what we really needed was generate multiple rows for multiple users…
Map (a bit like Linq)#
To loop over an array of user objects; rendering a UserRow for each one we found we could use javascript’s map function.
public render() { return ( <div> <h1>My Users</h1> <table className="user-list"> <tbody> {this.getUserData().map(user => <UserRow key={user.id} user={user} />)} </tbody> </table> </div> );}Not dissimilar to Select in C#, this will loop through the value returned from getUserData() and render a UserRow for each one.
If you’re wondering what the key attribute is, omit it and React will blow up. This is a special attribute which requires a unique value for each item in the array. React uses this to efficiently render each row and only re-render rows which have changed (when the source data changes).
Finally we could test this all out with a simple implementation of our getUserData() function.
private getUserData() { return [ { id: 1, name: 'Jon', summary: '36 / Lead Developer' }, { id: 2, name: 'Janine Smith', summary: '32 / Senior Engineer' } ];}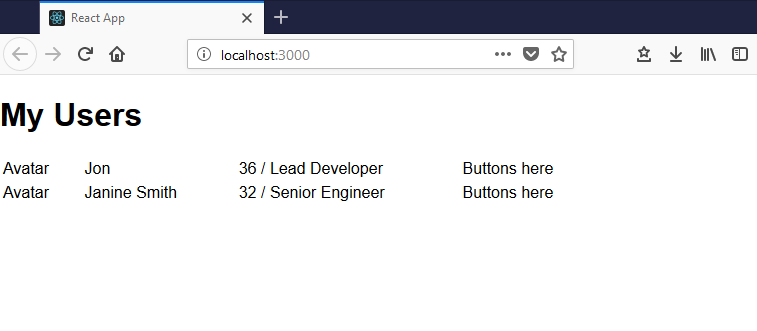
Summary#
Now our component was coming together.
We could render as many user rows as we had users; the next step would be to hook this up to our ASP.NET Core Web API.
All posts in Learning to use React with ASP.NET Core Web API
- Diary Of A Net Developer - Learning React
- Learning React - Building up the user interface using components and dummy data
- Learning React - How to connect React components to your ASP.NET Core Web API
- Learning React - Exercise control over your component state with Typescript
- Cross-Origin Request Blocked
Struggling to figure out what to focus on with Blazor?
BlazorSharp - The .NET Web Developers community is here to help!
- Connect with your fellow .NET web developers
- Keep up to date with the latest .NET changes
- Exchange tips, tools and tactics